Secure Monitoring and Control of Solar PV Systems through Dynamic Watermarking
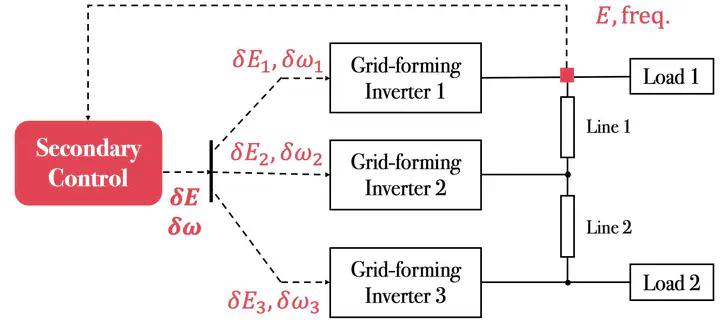 A microgrid with secondary controller
A microgrid with secondary controllerThis project will develop and demonstrate an active defense mechanism of cyber-resilient PV distribution system operation using a dynamic watermarking technique to monitor cybersecurity. The technique involves injecting a probe signal onto the grid to authenticate grid actions. The approach will include the real-time deployment of online computational algorithms in real-world critical locations. Partners include researchers from MIT, Texas A&M University, CenterPoint Energy, Argonne National Laboratory (ANL), and the Illinois Institute of Technology (IIT). The MIT team will develop corrective control algorithms to mitigate the negative impact of cyber attacks. The figure below presents the topology of a test microgrid with the secondary control. The secondary controller aims to regulate voltage magnitude and frequency at one bus of the microgrid by tuning the setpoints of all inverters. An attacker can compromise the microgrid by maliciously manipulating the telemetered measurements feeding the secondary controller. If it happens, all decisions made by the secondary controller will be wrong. To enhance the cyber resilience of the microgrid, key questions include: 1) how to detect the cyber attacks; and 2) how to mitigate the negative impacts of cyber attacks if the attacks are detected. The project teams leverage a dynamic watermarking approach to detect the cyber attacks. The MIT team are designing an observer-based approach for taking corrective actions once attacks are detected. With the proposed corrective controller, critical electrical variables can still be regulated in the presence of cyber attacks.
Funding Agency: US Department of Energy
